Multicast is a method of one-to-many device communication over an IP network.
Using RTP multicast, any number and combination of Algo IP devices including speakers, paging adapters, intercoms, and visual alerters can collectively broadcast a voice page announcement, ring event, emergency alert, scheduled bell, or background music. Multicast enables scalability in any Algo paging system to cover any sized room, building, or outdoor environment.
When using multicast, an Algo device can be set as a transmitter or receiver. Only the endpoint designated as the transmitter needs to be registered to the telephone system meaning receivers do not require SIP registration. This minimizes the costs associated with additional endpoint extensions in a hosted or cloud environment. IP endpoints configured as receivers require PoE and network connectivity wired as a home run to a networked PoE switch to receive multicast data packets. No additional Algo hardware or software is required.
Multicast uses minimal network bandwidth as only one copy of the network packets (~64kb) are sent from the transmitter regardless of how many receiver endpoints are listening to a given IP multicast zone.
Multicast Zones
Algo devices set as multicast receivers can be grouped into pre-configured zones to broadcast paging announcements or play alerts simultaneously. Multicast zoning is similar to how legacy channels are used in terms of their benefits, but they are different in terms of their setup. Legacy channels require the use of zone controllers and zone amplifiers, both of which are not necessary for multicast zoning. This means using multicast zones over legacy channels decreases the amount of wiring needed overall which can reduce costs.
In some cases, hybrid environments may be most ideal. This may be where legacy channels remain while new IP infrastructure is introduced and the two can work together. In this scenario, Algo paging adapters can be used.
Multicast zones can be created by using multicast IP addresses. Each multicast IP address configured in the transmitter endpoint will stream audio to the zone of configured receiver devices. Receiver devices can be members of any number of multicast zones.
Once configured, zones can be paged via:
DTMF Selectable Mode
Multiple SIP extensions.
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) refers to the sounds or tones a telephone generates when the numbers are pressed. To page with DTMF Selectable Mode, a user can dial the SIP extension of the transmitter device and dial the desired DTMF page zone (e.g., 1, 2, etc.) on the keypad.
If multiple registered SIP extensions are used, each extension is mapped to a unique zone allowing zones to be called directly.
Multicast IP Address
Each Algo IP device has a unique IP address and shares a common multicast IP and port number (multicast zone) for multicast packets. The transmitter device sends data to a configurable multicast zone, and the receiver units listen to its assigned multicast zones.
The network switches and router see the packet and deliver it to all zone receivers. The multicast IP and port number must be the same on all one zone’s transmitter and receiver units. Multiple zones may be defined by picking different multicast IP addresses and/or port numbers.
1. Multicast IP addresses range: 224.0.0.0/4 (from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255)
2. Port numbers range: from 1 to 65535
The default multicast IP address is set to: 224.0.2.60 port numbers 50000 – 50008
Ensure the multicast IP address and port number do not conflict with other services and devices on the same network.
Configuring Multicast on Algo Devices
Algo IP paging systems using multicast only require the first endpoint to be registered as a SIP extension. If only one audio stream is active at any given time, additional Algo IP endpoints, including any combination of paging adapters, speakers, and visual alerters, may be added as multicast receivers. If multiple unique audio streams are needed simultaneously, more than one transmitter will be required.
The Algo IP endpoint configured as the transmitter will stream audio to the receivers simultaneously. Receiver endpoints do not require SIP extensions and do not need to register with the SIP communication server.
For specific devices details, please see the product user guide.
Basic Multicast Settings
Basic multicast settings are used to set a device as a transmitter or receiver and other details that may be required for single zone paging. To configure basic multicast settings:
Log into the web interface by typing the device IP address into the web browser.
Navigate to Basic Settings → Multicast and check Transmitter (Sender) or Receiver (Listener) under Multicast Mode. Always ensure that the multicast settings on all receiver devices match those of the transmitter.
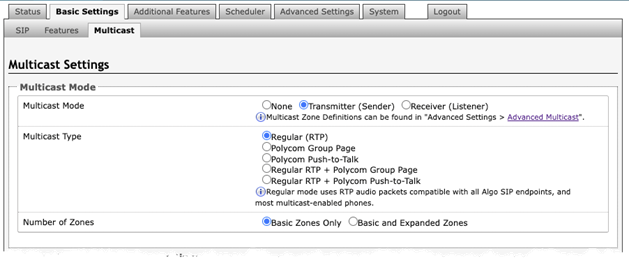
Multicast Mode
Multicast Mode
If Transmitter (Sender) is selected, the device will broadcast an IP stream when activated in addition to playing audio through the audio output.
If Receiver (Listener) mode is selected, the device will activate when receiving a multicast message. It will mimic the audio stream of the transmitter but use local volume settings. This can be set via Basic Settings → Features → Page Speaker Volume.
A device cannot be both a multicast Transmitter and Receiver simultaneously.
Multicast Type
The device may broadcast multicast paging compatible with Poly “on-premise group paging” protocol and most multicast-enabled phones that use RTP audio packets.
Select Regular (RTP) if you are only multicasting to Algo IP endpoints or multicast-enabled phones.
To multicast page announcements to Poly phones, select Poly Group Page or Poly Push-to-Talk.
Select Regular RTP + Poly Group Page or Regular RTP + Push-to-Talk to multicast page audio to Poly phones, Algo IP endpoints, and multicast-enabled phones.
Number of Zones
Select Basic Zones Only if configuring nine or fewer multicast zones.
Select Basic and Expanded Zones to configure up to 50 zones. The expanded zones have the same behavior as the basic Receiver zones but are hidden by default to simplify the interface.
Use the additional settings on the Multicast page to configure the device.
Poly Group Paging/Push-to-Talk This section is used if the Multicast Type includes Poly Group Page or Poly Push-to-Talk. | |
|---|---|
Poly Zone | Enter the same Multicast IP Address and Port number configured on the Poly phones. |
Poly Group Selection Mode | Select Single Group to broadcast on one pre-configured group. Multiple SIP extensions can be registered on the Transmitter device. Each extension is mapped to a unique group, allowing groups to be called directly (e.g., from speed-dial keys). See Additional Features → More Page Extensions for additional configuration settings. If DTMF Selectable Group is selected, the group is determined by the DTMF selection between 0 – 25. To page using DTMF Selectable Zone:
DTMF group definitions include:
…
All DTMF codes and respective zones are available in Advanced Settings → Advanced Multicast. |
Poly Default Channel | Select the default group for the multicast stream to be sent to. If DTMF Selectable Group is chosen, this single group setting will not apply to paging since the group will be dynamically selected per call using DTMF. The Single Group setting will still apply to the ring extension and relay triggered events. The Poly Default Channel is the default channel used for multicast actions unless an option is available for a custom channel with specific parameters. |
Speaker Playback Groups | Select Speaker Playback Groups to control which specific groups can play audio from the device. This is useful if using the DTMF Selectable Group mode or additional page extensions (Additional Features → More Page Extensions) per group to make the device a member of only certain zones. In this case, the Transmitter does not participate in the Zone but transmits certain traffic. |
Poly Receiver Channels | If using a Poly telephone as a Multicast Transmitter, a tone may be set for any of the 25 Poly Groups configured on the device. Poly Group Tones can be set in Advanced Settings → Advanced Multicast. The Poly telephone used as page audio source for the device must be configured to use either the G.711 or G.722 audio codec. Note that Poly phone(s) must be configured with the “Compatibility” setting (“ptt.compatibilityMode”) disabled for this codec setting to be applied. |
Transmitter (Sender) Zone Settings This section is used if the Multicast Type includes Regular (RTP). | |
|---|---|
Zone Selection Mode | Select Single Zone to broadcast on one pre-configured zone. Multiple SIP extensions can be registered on the Transmitter device. Each extension is mapped to a unique zone, allowing zones to be called directly (e.g., from speed-dial keys). See Additional Features → More Page Extensions for additional configuration settings. If DTMF Selectable Zone is selected, the zone is determined by the DTMF selection between 0 – 50. Once multicast Transmitter mode is enabled, navigate to Advanced Settings → Advanced Multicast to find the DTMF codes corresponding to each zone. To page using DTMF Selectable Zone:
DTMF zone definitions include:
All DTMF codes and respective zones are available in Advanced Settings Advanced Multicast. |
Transmitter Single Zone | Select the default zone for the multicast stream to be sent to. If DTMF Selectable Zone is chosen, this single zone setting will not apply to Paging since the zone will be dynamically selected per call using DTMF. However, this single zone setting will still apply to the ring extension and relay triggered events. The Transmitter Single Zone is the default zone used for multicast actions unless an option is available for a custom zone with specific parameters. |
Speaker Playback Zones | Select Speaker Playback Zones to control which specific zones the device can play audio. This is useful if using the DTMF Selectable Zone mode or additional page extensions (Additional Features → More Page Extensions) per zone to make the device a member of only certain zones. In this case, the Transmitter does not participate in the Zone but transmits certain traffic. |
DTMF Settings | |
|---|---|
Zone Selection Tone | Select a tone to be played to prompt a user to select a zone to multicast to. This may be used as an interactive voice response (IVR) menu by uploading a custom audio file in the tones folder through System → File Manager. Each zone may use a different tone. This can be configured in Advanced Settings → Advanced Multicast. |
Two-Digit Selection | When enabled, all DTMF Selectable Zones will require two digits. As a result, Basic Zones must be prefixed with 0, and Expanded Zones will no longer need to be prefixed with *. |
Receiver (Listener) Zone Settings | |
|---|---|
Basic Receiver Zones | Select one or more multicast zones for the device to listen to. Multicast zone priority will be based on the zone definition list order defined in Advanced Settings → Advanced Multicast. |
Expanded Receiver Zones | Select additional zones (up to 50) for the device to listen to. This is only possible when Basic and Expanded Zones is selected. |
Click Save when complete.
Test to confirm all devices are working as expected.
Advanced Multicast Configuration
Advanced multicast settings are used primarily for configuring multi-zone paging. To configure advanced settings multicast settings:
Open the web interface and navigate to Advanced Settings → Advanced Multicast.
Enable the desired zones under Basic Zone Definition and Expanded Zone Definition.
Set any additional configurations required.
Transmitter Settings | |
|---|---|
Transmitter Output Codec | Select an audio encoding format for the Transmitter device to use when sending output to the Receivers. Supported formats include:
|
Poly Output Codec | Select an audio encoding format when using Poly Group Page or Poly Push-to-Talk. Supported formats are G.711 ulaw and G.722 only. |
Output Packetization Time (milliseconds) | Select the size of the audio packets the Transmitter sends to the Receivers from the dropdown menu. The default of 20 milliseconds is recommended unless a different value is specifically required for compatibility with other devices. |
Multicast TTL | Only change the multicast time to live (TTL) setting if custom routing is configured on the network that specifically routes multicast packets between subnets and a longer TTL count is required. This ensures packets are not bounced back and forth in a network identity. When the TTL is reached, the router drops the packet. |
RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) | |
|---|---|
RTCP Port Selection | Select how a port will be chosen to send or receive RTCP packets. Note: If Next Higher Port is selected, ensure that the default multicast zone definitions are modified so that zones are only assigned to even-numbered ports, leaving the next higher odd-numbered ports free for RTCP packets. |
Receiver Settings | |
|---|---|
Audio Sync | Available if under Basic Settings → Multicast the Multicast Mode is set to Receiver (Listener) and Multicast Type is set to Poly Group Page or Poly Push-to-Talk. When using multicast with other third-party devices that have a delay in their audio path, the audio on the device may be heard slightly earlier than on these other devices. Use this feature to add a small delay to the audio output on the device to synchronize with these other devices. |
Polycom Receiver Tones | |
|---|---|
Poly Receiver Tones | Available if under Basic Settings → Multicast the Multicast Mode is set to Receiver (Listener) and Multicast Type is set to Poly Group Page or Poly Push-to-Talk. A tone may be set for any of the 25 Poly Groups. If using an Algo device as a Multicast Transmitter, it is recommended to set the Receiver tones to None to avoid conflicts, as the Algo devices already multicast a tone by default. |
Click Save when complete.
Multicast via Scheduled Events
The Algo 8301 IP Paging Adapter & Scheduler can be used to schedule event alerts such as school bells, break times, or other regular notifications. These event schedules can be configured for specific zones when the 8301 is set to a multicast transmitter. To do this:
Open the 8301 web interface.
Ensure the 8301 is set to Transmitter (Sender) under Basic Settings → Multicast.
Select the zones for the scheduled events to play in under Advanced Settings → Advanced Multicast.
Navigate to Scheduler → Schedules and enter the required scheduled events
Navigate to Scheduler → Calendar and apply the created schedules to the necessary days.
.png)
Audio Streaming via Multicast
Primarily used to play background music, this feature will multicast the input audio to the Sender Single Zone (located under Basic Settings à Multicast), as well as stream audio to the Line Out and Aux Out (if applicable).
Navigate to Additional Features → Input/Output tab and enable Audio Always On.
The input port and volume can be configured in the same tab.
In the Basic Settings → Multicast tab, select the Master Single Zone.
Note: A call to the page extension, alert extension, or scheduled event will interrupt the audio.
Adjusting TTL for Multicast Traffic
Algo IP endpoints configured as multicast transmitters use a TTL (time to live) of 1. This can be modified to allow more hops and prevent packets from being dropped.
To adjust this setting, navigate to System → Maintenance and select Download to Download Configuration File. Open the text file, search for “mcast.tx.ttl”, and set it to a value sufficient to handle the number of hops required. Save the file and upload it back to the unit.
Multicast Troubleshooting
Configuration Problems
Make sure the following settings match the configuration of your device (this is dependent on Multicast Mode setup).
Multicast Mode (Basic Settings → Multicast)
Sender = Transmitter
Receiver = Listener
Multicast Type (Basic Settings → Multicast)
Sender = Regular / RTP
Receiver = Regular / RTP
Zone Number (Basic Settings → Multicast)
Ensure the Zone # selected on the Sender is also ticked under the speaker playback zone on the Receiver. To have the page play on the Sender device, select the same zone for the Sender device itself.
A proper configuration will ensure the Receiver is listening to the Zone to which the Multicast packets are being sent.
Zone Definitions (Advanced Settings → Advanced Multicast)
Ensure the IP Address and Port # matches, on both the Sender and Receiver, for the zone being used.
Network Related Problems
If the configuration on the transmitter and receiver devices is correct, any remaining problem should be related to the local network. Below are some items to be aware of:
Ensure all devices in the Multicast Zone have IP addresses valid on the same subnet (if applicable).
Ensure all devices are in the same VLAN (if applicable).
Confirm all devices are reachable by paging them.
Make sure the network switches have Multicast enabled.